In the world of analytics, two terms always come to play; Dark Data and Big Data. Gartner Inc defined Dark Data as the information assets organizations’ collect, process, and store during regular business activities, but generally fail to use for other purposes. Gartner Inc also defined Big data as the high-volume, high-velocity, and high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective and innovative forms of information processing, which would usually enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation.
Dark Data vs. Big Data
By way of explanation, dark data is generated from system applications and system operations that aren’t analyzed or previously used to derive insights in decision making. On the other hand, Big Data is data that reveals information such as hidden patterns during production, which can help organizations in making informed business decisions capable of leading constructive business outcomes and intelligent business decisions.
Dark Data, through its vast collection of unstructured data, could hold valuable insights if it were to be organized, and subsequently analyzed. For instance, customer call records are Classified Dark Data. As discussed by Marica Tal, CEO of Tal Solutions on a recent podcast here, this can be analyzed to uncover deeper business trends, understand customer expectations, and make strategic decisions. Call details comprise of important information such as geolocation, customer preferences, product reviews, etc. All this data may be useful for companies to observe customer engagement patterns and accordingly improve their services.
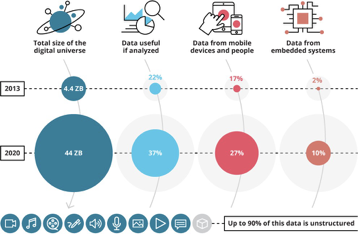
Big Data is also most useful if it’s being analyzed; It comprises semi-structured and structured data. Companies like YouTube, Microsoft, Google, and co are foremost when it comes to analyzing big data, and they use the resulting knowledge to gain a competitive advantage in the tech market.
Take a look at Youtube’s recommendation system; the company takes all your watching history together with what it knows about you, such as your location, most liked videos, the genre of videos you watch more, etc. It then comes up with some pretty good suggestions that are likely to interest you as recommendations on your home page.
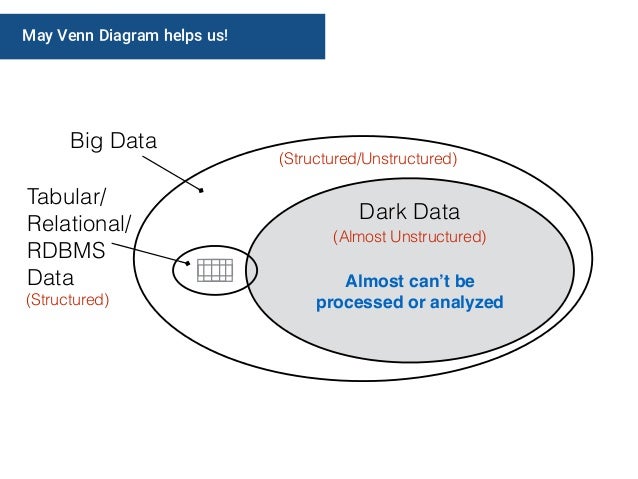
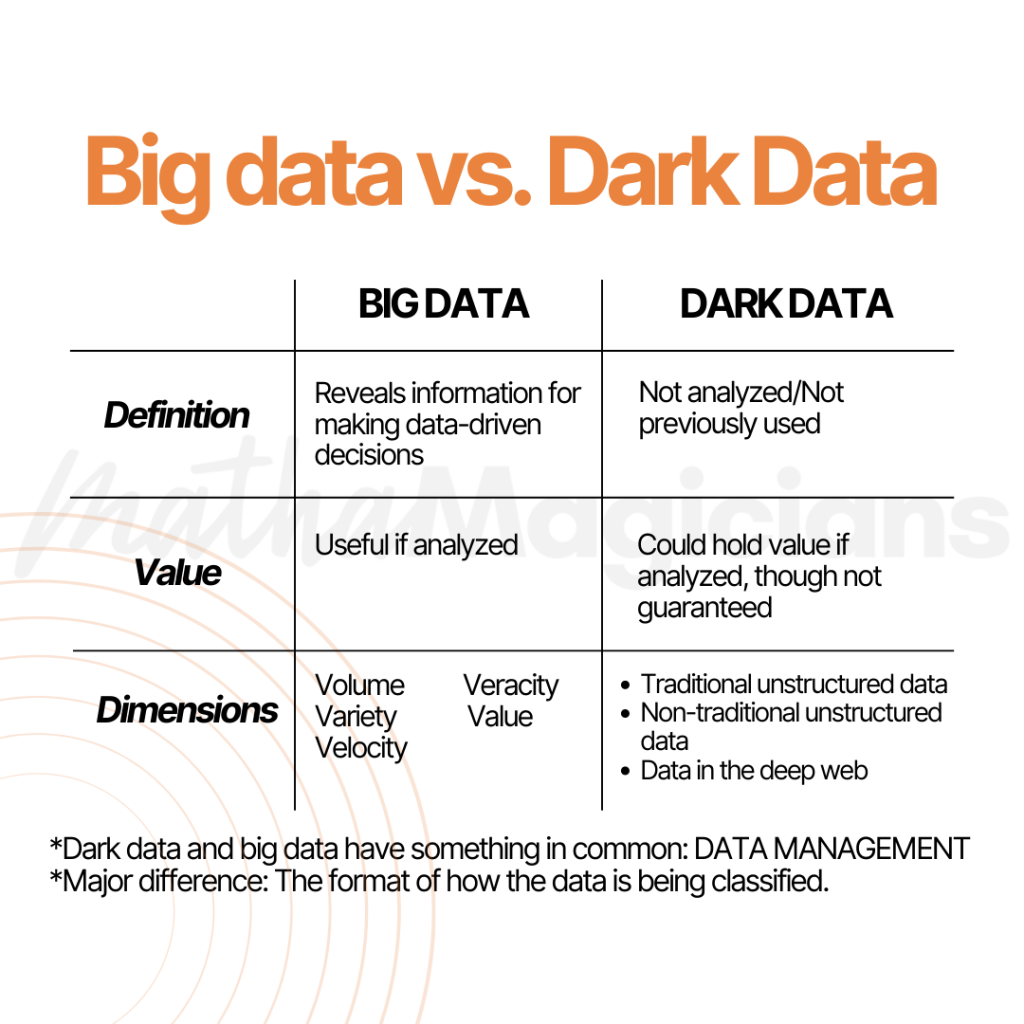
In effect, dark data and big data have something in common, which is data management, and the major difference is in the format of how the data is being classified.
Dimensions of Dark Data
Dark Data comprises of three dimensions:
- Traditional unstructured data: Includes Data that is already present within an organization’s cache. Emails, documents, messages are a few examples.
- Non-traditional unstructured data: These include unstructured data such as image, audio, and video files that cannot be processed or analyzed with traditional analytics techniques
- Data in the deep web: This is the largest body of unexploited data. The deep web comprises an incredible amount of data curated by academics, government agencies, third-party domains. The perceptible lack of structure is the key factor that makes it difficult to search on the deep web.
Dimensions of Big Data
Big Data is grouped into five dimensions:
- Volume: refers to the quantity of data, as big data is frequently defined in terms of massive data sets with measures such as petabytes and zettabytes etc.
- Variety: Refers to the diversified sources and types of data requiring management and analysis, such as databases.
- Velocity: It has to do with the accelerating speed at which data flows in from various sources like production processes, internet networks, social media sites, etc.
- Veracity: refers to the biases, noise, and irregularity in data being generated.
- Value: refers to the ability to transform a large chunk of data into business.
This 5V’s is a data management trend that was conceived to help organizations realize and cope with the emergence of big data.
Dark Data and Big Data in the present World
For any business, data is vital; it holds the key to attracting new customers, increasing growth, and creating bigger profits, that’s why both Dark Data and Big Data are big elements in the analytics world. At first glance, the obstacles to finding and harnessing dark data can seem too big to overcome, but there has been a huge rise in the importance of Dark Data in the present World of analytics. It holds a massive amount of potential for those who want to harness its immense power and move this information into critical datasets. Big Data has been around for a while, characterized by large and complex data sets. Tools such as Apache Spark, Pig, Hadoop, Hive, Cassandra, Kafka have been used when working with Big Data.
For making better decisions, organizations join structured and unstructured data sets together, to provide high-value results. When done correctly, the benefits will easily outweigh the costs involved with mining these datasets.
What awaits us in the future?
The vast majority of the World’s population uses the internet. Each one of our activities on the internet, even if it seems insignificant, leaves a digital footprint. With this information, we can better understand user behaviour, and new business opportunities can be identified going forward. There is nothing dark about dark data, as the ecosystem for data and AI further develops, we will continue to find new and innovative ways to make it useful and impactful for our lives.









Add Comment